One of the most significant environmental considerations within a laboratory is its air quality and the safety measures provided by the in-lab equipment. Whether you buy new equipment, or are looking to source refurbished or pre-owned laboratory equipment, understanding how to treat hazardous fumes and particulate, could help in your sourcing decisions. Two types of equipment, that deal with providing in-lab personnel and environmental protection, are the Chemical Fume Hood and the biological safety cabinet. Both are commonly referred to as “hoods”, however they are two different classes of lab equipment. Here’s what you should know about them when deciding which to purchase.
Understanding the Difference
Because of their cursorily-similar application, it’s common to hear less experienced laboratory staff refer to a biosafety cabinet as a “fume hood”. While they both address hazards within a laboratory environment, technically, these are two separate classes of lab equipment in the types of protection they deliver. The critical distinction, however, is that the latter (fume hoods) deliver only personal protection to staff working under them – or in their proximity; while the latter (biological safety cabinets) offer a broader range of protection, including product/samples, personnel, and environmental safety.
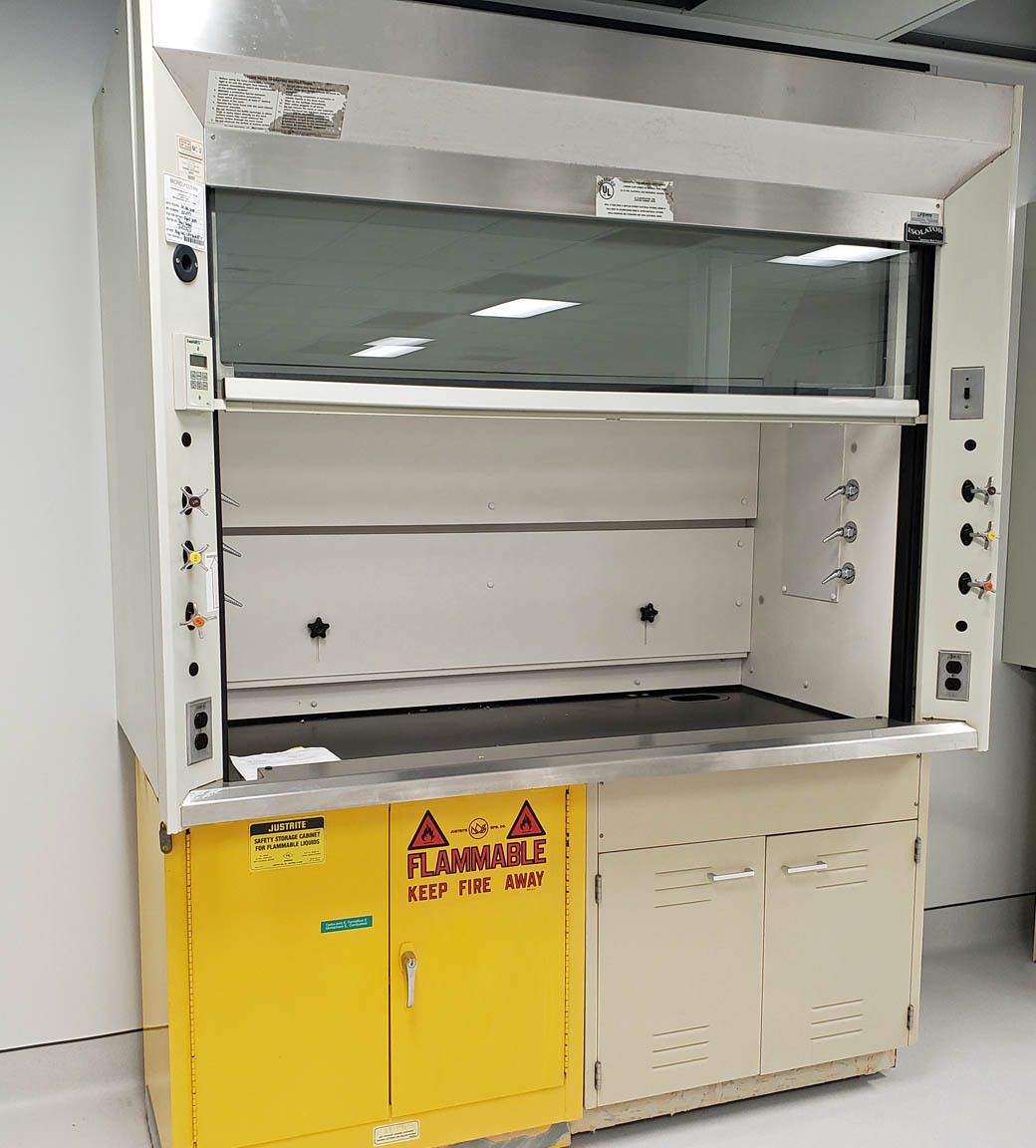

When a lab technician works under a fume hood, he/she receives the protection of a ventilated enclosure. The enclosure quickly, and efficiently, deals with any volatile vapors and/or chemical fumes, that might result from the operator’s experiment or test, and removes them (vapors/fumes) from the area, providing personnel safety to the attendant conducting the test/experiment.
A biological safety cabinet has a much broader scope of safety and protection application. It uses high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters to deliver protection that expands wider than just personnel protection, to include sample and product safety, as well as environmental safety. Depending on your unique laboratory environment (or application), you may choose a biosafety cabinet that either exhausts or recirculate the filtered air. You may also choose the types of hazardous particulates you wish to protect against, such as viruses or bacteria.
Understanding Airflow
Both, a fume hood and biological safety cabinet, provide safe operating environments by regulating how air flows work. In the case of the former, the fume hood draws air away from the operator/technician, beginning at the face (“door”) of the equipment. The hazardous fumes are pulled across the countertop/work area, sucked into the duct, and then released outdoors.
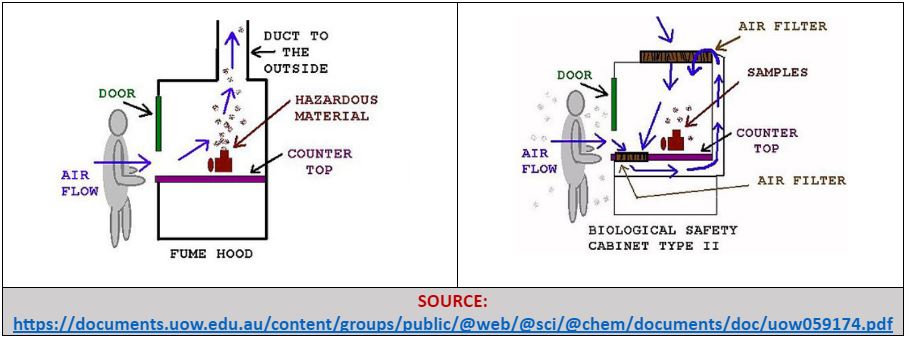
Airflow treatment in a biosafety cabinet depends on the type of cabinet installed in your laboratory – Class I, II or III. In the case of a Class II cabinet, for instance, it pulls air safely around the attendant/lab worker through intake fans, while sterile air, filtered through a HEPA filter, is then flowed downward, and recirculated into the laboratory environment. Alternatively, the filtered air may be released into the atmosphere through the labs ducting system.
Making the Right Choice
When it comes to deciding which of the two solutions you need – a fume hood versus a biological safety cabinet, there’s no one size fits all choice. It all depends on the application. When sourcing used or refurbished laboratory equipment, however, it’s vital to know what to look for. In most laboratories, both, hoods, and cabinets, are a standard part of lab layout.